一、介绍
特点
栈(Stack)是一种特殊的线性表,它只允许在一端进行插入或删除操作。这一端被称为栈顶(Top),而固定的另一端则称为栈底(Bottom)。栈的特点是后进先出(Last In First Out,简称LIFO),即最后插入的元素将会是第一个被删除的元素。
结构
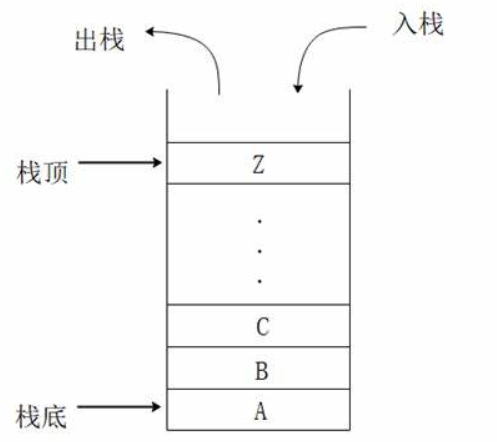
二、实现
在stack.h中需要声明的头文件
#include <stdio.h>
//malloc函数用到
#include <stdlib.h>
//assert函数用到
#include <assert.h>
栈结构
在List.h中声明
typedef int StackDate;
typedef struct stack
{
//动态栈
StackDate* _a;
//栈内的数据的数量
int _top;
//栈的大小
int _capscity;
}stack;
初始化跟销毁
//初始化跟销毁
void Stack_init(stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
//初始化给四个数据空间
pst->_a = (StackDate*)malloc(4*sizeof(StackDate));
pst->_top = 0;
pst->_capscity = 4;
}
void Stack_destory(stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->_a);
pst->_a = NULL;
pst->_capscity = pst->_top = 0;
}
入栈
void Stack_push(stack* pst,StackDate x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->_top == pst->_capscity)
pst->_capscity *= 2;
StackDate* tmp = (StackDate*)realloc(pst->_a, sizeof(stack) * pst->_capscity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("内存不足!");
exit(-1);
}
else pst->_a = tmp;
pst->_a[pst->_top++] = x;
}
出栈
void Stack_pop(stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->_top > 0);
pst->_top--;
}
获取数据个数
int Stack_size(stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->_top;
}
检查是否为空
//返回1是空,返回0是非空
int Stack_empty(stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return !pst->_top;
}
获取栈顶数据
StackDate Stack_top(stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->_top > 0);
return pst->_a[pst->_top - 1];
}
三、代码
stack.h文件
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
//malloc函数用到
#include <stdlib.h>
//assert函数用到
#include <assert.h>
typedef int StackDate;
typedef struct stack
{
//动态栈
StackDate* _a;
//栈内的数据的数量
int _top;
//栈的大小
int _capscity;
}stack;
//初始化跟销毁
void Stack_init(stack* pst);
void Stack_destory(stack* pst);
//入栈
void Stack_push(stack* pst, StackDate x);
//出栈
void Stack_pop(stack* pst);
//获取数据个数
int Stack_size(stack* pst);
//返回1是空,返回0是非空
int Stack_empty(stack* pst);
//获取栈顶的数据
StackDate Stack_top(stack* pst);
stack.cpp文件
#include"stack.h"
//初始化跟销毁
void Stack_init(stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->_a = (StackDate*)malloc(4*sizeof(StackDate));
pst->_top = 0;
pst->_capscity = 4;
}
void Stack_destory(stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->_a);
pst->_a = NULL;
pst->_capscity = pst->_top = 0;
}
//入栈
void Stack_push(stack* pst,StackDate x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->_top == pst->_capscity)
pst->_capscity *= 2;
StackDate* tmp = (StackDate*)realloc(pst->_a, sizeof(stack) * pst->_capscity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("内存不足!");
exit(-1);
}
else pst->_a = tmp;
pst->_a[pst->_top++] = x;
}
//出栈
void Stack_pop(stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->_top > 0);
pst->_top--;
}
//获取数据个数
int Stack_size(stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->_top;
}
//返回1是空,返回0是非空
int Stack_empty(stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return !pst->_top;
}
//获取栈顶的数据
StackDate Stack_top(stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->_top > 0);
return pst->_a[pst->_top - 1];
}
main.cpp文件
#include"stack.h"
void test()
{
stack st;
Stack_init(&st);
Stack_push(&st,1);
Stack_push(&st, 2);
Stack_push(&st, 3);
Stack_push(&st, 8);
Stack_push(&st, 5);
Stack_pop(&st);
printf("%d\n", Stack_top(&st));
printf("%d\n", Stack_empty(&st));
printf("%d\n", Stack_size(&st));
}
int main()
{
test();
}

